
Understanding Medicare
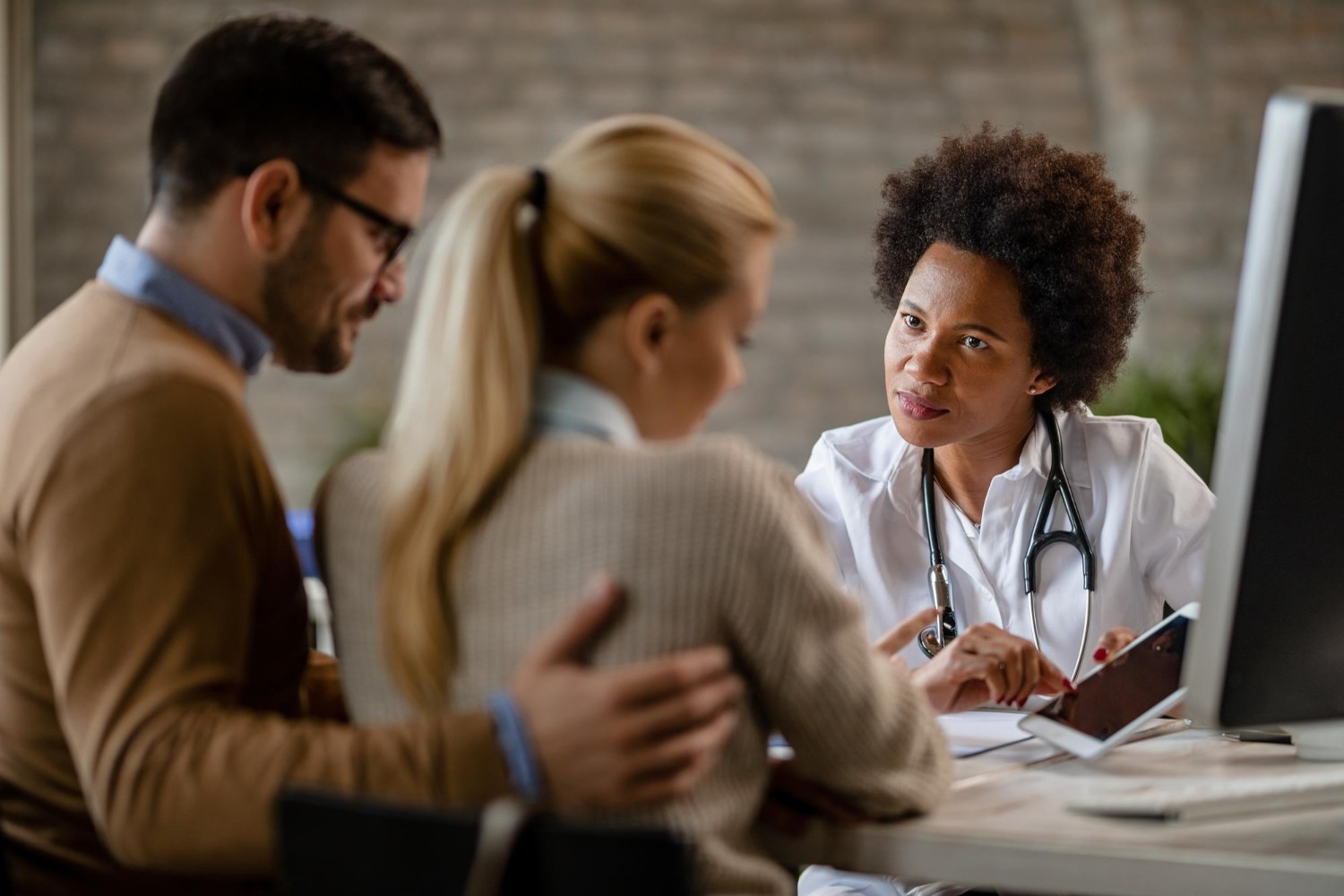
Medicare is a national health insurance program in the United States that provides coverage for eligible individuals who are 65 years of age or older, or who have certain disabilities or end-stage renal disease. It was created in 1965 as part of the Social Security Act to provide health insurance to older Americans who could not afford private insurance.
There are four parts of Medicare: Part A, Part B, Part C, and Part D. Part A, also known as Hospital Insurance, provides coverage for inpatient hospital care, skilled nursing facility care, hospice care, and home health care services. Part B, also known as Medical Insurance, provides coverage for doctor visits, outpatient care, and preventive services. Part C, also known as Medicare Advantage, allows individuals to receive their Medicare benefits through private insurance companies. Part D provides coverage for prescription drugs.
Most individuals are automatically enrolled in Medicare Part A and Part B when they turn 65 years old. If an individual is not automatically enrolled, they can enroll during their Initial Enrollment Period, which is the seven-month period that begins three months before they turn 65.
While Medicare covers many medical expenses, it does not cover everything. Individuals may still be responsible for deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance costs. Additionally, some services, such as dental care, vision care, and hearing aids, are not covered under Medicare.
Overall, Medicare plays a crucial role in providing health insurance coverage for older Americans and individuals with certain disabilities or end-stage renal disease. Regenerate response

Hospital Insurance:
covers things like inpatient hospital stays, home health care and some skilled nursing facility care. Together, Medicare Parts A and B are called Original Medicare.

Medical Insurance
covers things like doctor visits, outpatient services, X-rays and lab tests, and preventive screenings.
Medicare Advantage
Private health insurance companies offer these plans. When you join a Medicare Advantage plan, you still have Medicare. The difference is the plan covers and pays for your services instead of Original Medicare.

Prescription Drug Coverage
Medicare Part D is an outpatient prescription drug coverage. To get drug coverage you must join a Medicare-approved plan, such as a Medicare Advantage plan with drug coverage
